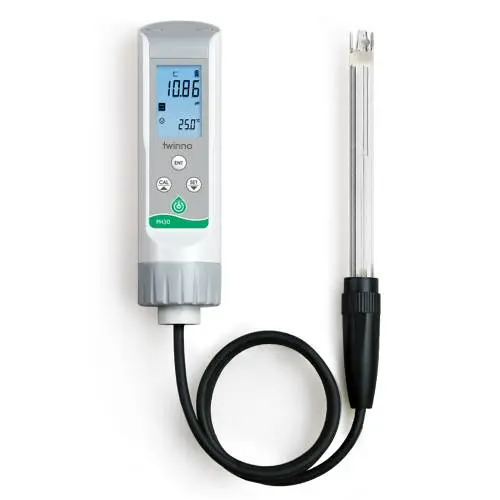
Accurate pH measurement is essential in field testing for environmental monitoring, water quality assessment, and research applications. Field conditions can be unpredictable, and obtaining reliable data requires instruments that are both precise and robust. A water pH sensor provides real-time measurements that allow researchers and field operators to make informed decisions and maintain data integrity.
Importance of Accurate pH Measurement in Field Testing
In environmental and water quality studies, pH serves as a key indicator of chemical balance, pollution levels, and ecosystem health. Small deviations in pH readings can lead to incorrect conclusions, potentially impacting environmental management decisions. A water ph sensor enables accurate monitoring under varying field conditions by converting hydrogen ion activity into measurable electrical signals, ensuring consistent and trustworthy data collection.
How a Water pH Sensor Works in Field Conditions
A water pH sensor typically contains a measuring electrode that interacts with hydrogen ions in the sample and a reference electrode that provides a stable baseline. The voltage difference generated between these electrodes is then converted into a pH value, which can be displayed directly or recorded in a data logging system.
Field-ready sensors are designed to withstand temperature fluctuations, exposure to sediments, and other environmental challenges. Many models include automatic temperature compensation, which ensures that pH readings remain accurate despite changes in water temperature commonly encountered in lakes, rivers, or groundwater sampling sites.
Applications in Environmental Monitoring
Water pH sensors are widely used in environmental field testing to assess rivers, lakes, wetlands, and groundwater. They help detect acidic or alkaline conditions caused by industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, or natural processes. Continuous monitoring allows field operators to respond quickly to abnormal pH levels, enabling early intervention to protect ecosystems and comply with environmental regulations.
In addition, pH sensors support soil and sediment testing in agricultural and ecological studies. Accurate pH measurements provide insights into nutrient availability, soil health, and the suitability of habitats for plants and microorganisms.
Benefits in Research and Field Studies
Reliable pH data enhances research accuracy, allowing scientists to analyze chemical interactions, biological processes, and environmental trends with confidence. A water pH sensor reduces human error compared to manual titration methods and allows for continuous data collection over extended periods. This capability is particularly valuable in long-term monitoring projects or remote field sites where repeated sampling is challenging.
Integration With Data Logging and Automated Systems
Modern field testing often involves portable data loggers or integrated monitoring systems. Water pH sensors can transmit real-time measurements to these devices, enabling continuous recording, trend analysis, and remote monitoring. Automated alerts can be set to notify operators when pH deviates from acceptable ranges, ensuring timely corrective action.
Such integration improves efficiency, reduces manual labor, and provides a robust data trail for scientific reporting, regulatory compliance, and decision-making.
Factors That Affect Accuracy in the Field
To maintain high accuracy, field operators must consider several factors. Proper calibration using standard buffer solutions is essential. Cleaning and maintenance of electrodes help prevent fouling from sediments, organic matter, or chemical residues. Extreme temperature fluctuations or prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals may also affect readings, making durable sensor construction and temperature compensation features critical for field applications.
Selecting a sensor designed for field use, following proper calibration procedures, and implementing maintenance best practices ensures reliable data collection in even the most challenging environments.
Conclusion
A water pH sensor significantly improves data accuracy in field testing by providing precise, real-time pH measurements under diverse environmental conditions. Its use reduces human error, supports continuous monitoring, and enables timely decision-making in environmental research, water quality management, and field studies. By choosing the right sensor, maintaining proper calibration, and integrating it with automated systems, field operators can achieve high-quality, reliable data that informs sustainable practices and scientific investigations.